The increasing digitalisation of critical infrastructures, including electrical substations, requires the implementation of more and more advanced communication solutions. Traditional systems based on analogue data transmission methods are becoming insufficient in the face of growing demands for reliability, responsiveness and operational safety.
Process bus in modern electrical substations
The process bus is a key element of modernisation in the electricity sector. It is a fundamental solution enabling digital data transmission in accordance with the IEC 61850 standard. It allows for the replacement of traditional copper cabling with Ethernet infrastructure, which leads to significant improvements in the operation of electrical power systems.
One of the key aspects of modern process bus implementations is also the use of 10 Gbps uplink links, which ensure adequate performance and determinism of transmitted data. The increase in the amount of transmitted information and the growing number of measuring devices require the use of faster connections that eliminate the limitations of the existing 1 Gbps systems.
What is a process bus and how does it work?
A process bus is a digital communication layer that enables data exchange between field devices and control devices in a substation. It is one of the key pillars of the IEC 61850 standard, which defines the communication method between intelligent electronic devices (IEDs).
Traditionally, measurements and control in electrical substations were carried out using copper cables connecting current and voltage transformers (CT/VT) to protective relays. However, this solution had many disadvantages, such as high installation costs, susceptibility to electromagnetic interference and limited flexibility in the event of system expansion. The process bus eliminates the need for analogue connections and replaces them with an Ethernet network in which
- measurement data is transmitted in the form of digital sampled values (SV),
- control and protection signals are transmitted using the Generic Object Oriented Substation Event (GOOSE) protocol.
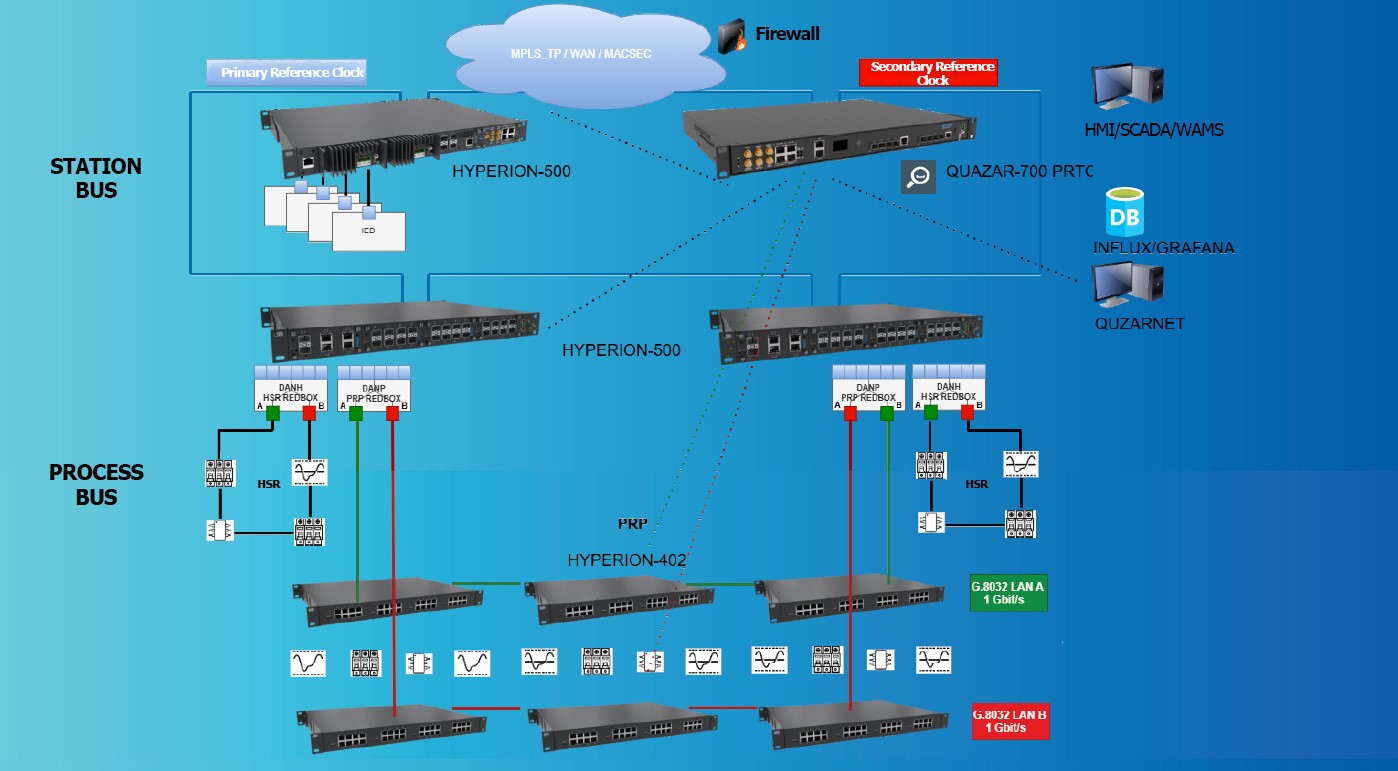
Station architecture IEC 61850 for transmission and time synchronisation with monitoring, based on BitStream solutions, photo: BitStream
This means that analogue data is converted to digital form at the field device level and then transmitted to the control devices via Ethernet. This approach not only simplifies the system architecture, but also increases its reliability and reduces the risk of operational errors.
Benefits of using a process bus
Reduction of installation and maintenance costs – one of the main reasons for implementing a process bus is to reduce the costs associated with installing and maintaining the cable infrastructure. In traditional solutions, each measuring line required separate copper wires to be routed, which increased material and labour costs. Using a process bus eliminates the need to build these costly connections, which allows for:
- reducing the amount of materials used (copper, insulation, cable trays),
- shortening the system installation and implementation time,
- minimising the risk of connection errors resulting from physical defects in the cables.
Greater flexibility and scalability - the process bus allows for easy system expansion by adding new devices without the need for additional cables. In IEC 61850-based solutions, a software configuration is all that is needed to add a new measuring point or protection device, if the synchronisation chain allows it. This significantly speeds up the modernisation process and reduces its costs.
Greater reliability and resistance to failures - traditional systems are susceptible to electromagnetic interference and physical damage to cables. A process bus based on fibre-optic data transmission eliminates these problems and ensures:
- resistance to electromagnetic interference occurring in HV and LV stations,
- better signal transmission quality thanks to digital data transmission,
- connection redundancy, which allows for reliable operation even in the event of a single link failure.

BitStream solutions, photo: BitStream
IEC 61850 process bus with 10 Gbps bandwidth – a necessity or an excess?
As a bitstream provider, we can see that the digital transformation in the Polish power sector is gaining momentum. Traditional systems based on analogue connections are being replaced by modern, digital transmission networks compliant with IEC 61850, which means the emergence of the aforementioned process bus, which enables direct transmission of sampled SV measurement values and control messages (GOOSE) via Ethernet.
The commonly used bandwidth of 1 Gbps, although still useful, is starting to become a limitation in transmission systems. The increased number of measurements and the increase in sampling frequency generate an ever-greater demand for bandwidth. For example, for 110, 220 and 400kV substations, where many optical and traditional transformers are used, the number of samples per second can exceed 16,000 per measuring point. An increase in the sampling frequency (e.g. 256 samples per cycle) causes the data stream to grow, and 1 Gbps is no longer sufficient. The introduction of 10 Gbps in the process bus allows for:
- reducing delays in the transmission of critical measurement data,
- supporting a greater number of devices without the risk of network overload,
- improving transmission determinism through the implementation of TSN (Time-Sensitive Networking),
- implementing full redundancy in power grid security communications, eliminating potential points of failure.
As a result, 10 Gbps becomes a standard that not only meets current needs, but also prepares the infrastructure for future requirements related to the development of smart power grids.
Process bus in summary
The process bus is the foundation of modern substations, eliminating analogue connections in favour of digital data transmission. Its implementation increases reliability, reduces costs and simplifies maintenance. At the same time, the use of 10 Gbps in the process bus allows for deterministic transmission, elimination of delays and support for a larger number of devices, making it an indispensable standard in modern power engineering. Bitstream has both the knowledge and the right products to support this transformation. With our solutions, which are tailored to the IEC 61850 standard and the modern requirements of the process bus, we can help you build fully digital, scalable and efficient substations. We offer industrial switches, synchronisation devices and communication parameter monitoring systems that enable the implementation of infrastructure that meets the highest technological and safety standards.
As Bitstream, we not only follow the development of digitalisation, but also actively participate in it by offering advanced network solutions for critical infrastructure. Our experience and technologies allow our customers to build the future of the power industry in a reliable, scalable and future-proof way.
Maciej Tomczyszyn
Marketing and Sales Manager Bitstream
Source: Energetyka.plus











