Smart phones (smartphones). Smart businesses. Smart homes. The need for a new mobile network standard arose not only through the huge (and ever-increasing) number of users and equipment, but also the ever-increasing demands and requirements for fast and stable connectivity. This is how the fifth-generation mobile network – 5G – came into being. 5G was designed not only to solve the problems of its predecessor, 4G LTE, but also to enable a continuous expansion of its capabilities. This approach was aimed at improving the user experience and enabling the use of the mobile network in entirely new service areas. The technological leap that will be achieved with the commercialisation of 5G will open up previously unattainable possibilities. Fully autonomous Industry 4.0 will be able to become a reality. Why?
5 reasons why 5G is the inevitable future
- Much higher transmission speeds. A 5G network can offer from an average download speed of 1Gbps to as much as 20Gbps in city centres. 4G, on the other hand, typically provides speeds of up to 100Mbps, which is at least 10 times slower transmission.
- Significantly lower latency. The average latency of a 5G network is 5 times lower than that offered by a 4G network (5G – around 10ms, 4G – around 50ms). Ultimately, 5G network latency is to be reduced to as low as 1ms.
- Greater network capacity. 5G has a much higher capacity – the network can support up to 1 million devices per square kilometre. Compared to LTE and a network capacity of up to 250 devices per sector or 750 per base station, 5G has a considerable advantage.
- A unified platform with greater capabilities. The 5G network has been designed to not only increase the efficiency of the services provided, but also to serve entirely new areas of service. The flexibility of the 5G network, through the use of all types of spectrum and bands, new ways of connecting and different deployment models, will allow for completely new business models.
- Splitting networks as required. The 5G network architecture allows specialised virtual networks (network slice) to be divided up on a shared infrastructure. The concept will allow the separation of individual network “slices” for specific applications or customers and the provision of services with highly differentiated transmission parameters such as special security or individual services.
Applications of 5G networks in industry and business
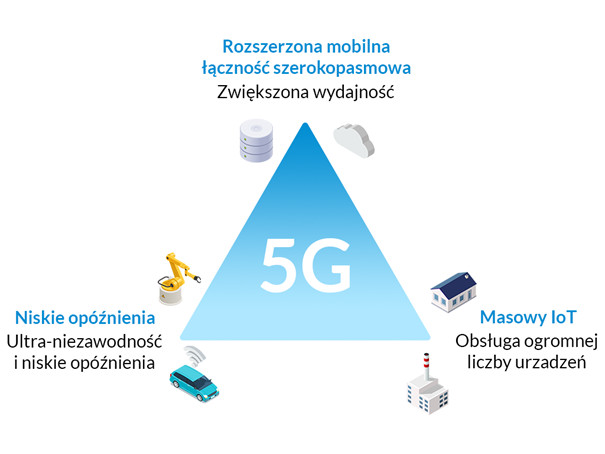
The commercialisation of 5G will have a decisive impact on global markets. By taking a developmental approach to the standard and placing great emphasis on the compatibility of future services, 5G will create the conditions for the introduction of entirely new types of services that have not previously been possible or have not yet even been invented. Based on already existing technologies and industries, it is possible to identify 3 main areas (the so-called 5G triangle) that will benefit most from the spread of this technology:
- Enhanced mobile broadband, requiring constant availability and high transmission speeds.
- Mass machine-type communication, supporting a very large number of devices.
- Ultra-reliable, low-latency, mission-critical communication.